Enter your address to receive notifications about new posts to your email.
Science & Publishing
-
Science & Publishing
Fine-Mapping Diabetic Traits with Outbred Rats
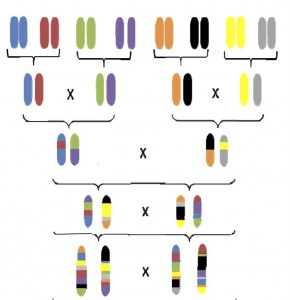
In 1979, as the US slid into recession, researchers began systematically crossing eight distinct inbred rat strains. Their goal was to establish a genetically diverse rat colony to serve as a base for phenotype measurements and artificial selection. But the creators of the NIH rat Heterogeneous Stocks (HS) faced major challenges: “…the main one being…
-
Science & Publishing
Frog immune responses to a global threat
Dramatic global declines in amphibians have been linked to the fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, but some species are more vulnerable than others. In the latest issue of G3: Genes|Genomes|Genetics, as part of the GSA Journals’ Genetics of Immunity collection, Ellison et al. examined the transcriptome of the highly susceptible Panama Golden Frog after exposure to…
-
Science & Publishing
Does neural crest development drive domestication syndrome?
In Stellenbosch, South Africa, in the shade of the university botanical gardens, Adam Wilkins and Richard Wrangham drank coffee and worked their way through a list. Tameness. Smaller muzzles. Smaller teeth. Patches of white fur. Floppy ears. In early 2011, Wilkins, Perspectives editor at GENETICS, and Wrangham, primatologist at Harvard, were both spending the semester…
-
Science & Publishing
Genetic maps, 100 years later
One feverish night, just over 100 years ago, an undergraduate in Thomas Hunt Morgan’s lab created the first genetic map. Realizing that the frequency of crossing over could be used to work out out the linear order of genes on a chromosome, that student, Alfred Sturtevant, published his map in 1913 and laid the foundation…
-
Science & Publishing
Turning to the Worm
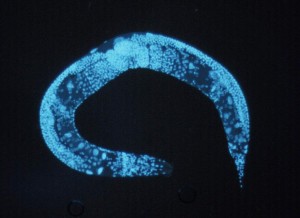
When Scott Alper and colleagues looked for candidate regulators of mammalian innate immunity based on gene expression data, the hit rate was only around 2%. By using a comparative genomics approach — starting with an RNAi screen in Caenorhabditis elegans — their hit rate rose to nearly 30%. In a new GENETICS article, published as…
-
Science & Publishing
The Fragile Y
Y chromosomes have come and gone many times during evolutionary history. Take beetles. When Heath Blackmon and Jeff Demuth modeled sex chromosome evolution in more than a thousand beetle species, they found the Y chromosome had independently evolved around 65 times in the suborder Adephaga alone. And as fast as this group evolved new Y chromosomes,…
-
Science & Publishing
More Bang for your GWAS Buck
For genome-wide association studies, data is power. The more data you have, the more statistical power you wield to find genetic associations. But are there ways to get more from the data you already have? In the May issue of GENETICS, Kaufman and Rosset describe a testing framework that substantially boosts the power of genome-wide…
-
Science & Publishing
GSA Journals Spotlight 2013
The GSA Journals, GENETICS and G3: Genes|Genomes|Genetics, are proud to present our annual Spotlight booklets for research published in 2013. Each Spotlight is a showcase of the excellent research and scholarship published over the course of the year, along with a selection of striking images submitted by our authors. Browse the 2013 GENETICS Spotlight. Browse the 2013 G3 Spotlight.
-
Science & Publishing
Neanderthal Relations: Interbreeding or Ancestral Structure?
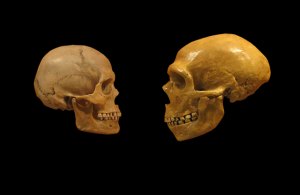
In Eurasia, humans once had Neanderthals for neighbors. That time of co-existence seems to have left its marks in our genome; non-Africans today share more genetic variants with Neanderthals than Africans do. But does this really mean there was interbreeding between humans and the Hominids next door? Some have previously proposed an alternative explanation for that…
-
Science & Publishing
New Fish on the Block
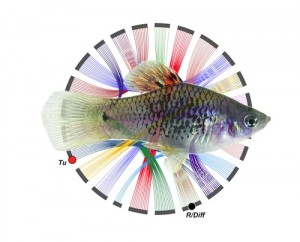
The medaka, or Japanese rice fish, is a century-old genetic model on the rise again. Long studied by scientists in Japan, it has been rediscovered by the wider research community over the last decade as a flexible tool for vertebrate genetics. Part of the appeal is the medaka’s amenability to inbreeding. In the latest issue…
-
Science & Publishing
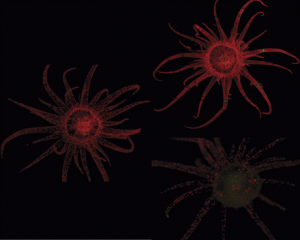
Sea Anemone & Friends
Coral reefs around the world are “bleaching”, a threat caused by breakdown of the symbiosis between the coral animals (cnidaria) and the dinoflagellate algae that live within their cells. Yet this crucial symbiotic partnership is poorly understood. To address this knowledge gap, biologists are developing a suite of genomic tools for the sea anemone Aiptasia. This…