Enter your address to receive notifications about new posts to your email.
Articles tagged Fundamental Research
(130 results)
-
Off-balance mice shed light on inner ear development
The “hyperspin” long-range enhancer deletion recapitulates disease phenotypes. In recent years, improvements in genetic testing have made it much easier to discover the causes of rare genetic diseases, but sequence data can also present new puzzles. Take split hand/-foot malformation-1 syndrome (SHFM1), which causes limb deformities, such as joined fingers, and sometimes deafness. Candidate culprits…
-
Seeking the flaw in error-prone DNA polymerases
Yeast study suggests faulty proofreading is not to blame for link between cancer and DNA polymerase ε variants. Accurate DNA replication is a matter of life and death. The polymerases responsible for replicating DNA have built-in safeguards to defend genome integrity, including proofreading activities to correct their own errors. Abnormally error-prone variants of DNA polymerase…
-
Alternative splicing tunes sex differences in flies
The Y chromosome has an unanticipated role in sex-biased intron retention in Drosophila. Differences between males and females in sexually dimorphic species stem in part from disparities in gene expression. This sex-biased expression can be achieved through numerous means, one of which is alternative splicing. In a recent study, Wang et al. investigated differences in one…
-
Why Ciliates? Making a video introduction to a model organism
Model organism researchers face shared challenges in communicating the value of their work. How do you get policymakers to fund research on a microscopic organism they’ve never heard of? How do you explain to the public why scientists spend time understanding yeast and frogs and flies? In 2015, the ciliate research community decided to invest…
-
A new role for a signpost on the chromatin landscape
Monomethylated H3K27 is more than just an intermediate. We often talk about biological traits as if they’re written in our DNA, but some of them aren’t in our DNA at all—instead, they’re on it in the form of chemical tags on the histone proteins our genomic DNA is wrapped around. During development, each cell’s genome…
-
On the origin of germ cells
Recent evolution of simple germ–soma division in a green alga sheds light on the early stages of complex multicellular life. Among evolution’s greatest innovations are germ cells. These specialized reproductive cells—familiar to us as sperm and eggs in humans—set the stage for complex multicellular life because they free up all the other cells in the…
-
The genomic downside of greener pastures
Population data from Quebec reveals the genetic consequences of rapid human expansions. The majority of the 6.5 million French Canadians living in Quebec today can trace their heritage to just 8500 settlers who formed clusters around the Saint Lawrence River in the early 17th century. Most remained near those riverside settlements until 200 years later,…
-
Giant milkweed genome grows drug potential
Shrub rich in potentially anticancer and antimalarial cardenolide compounds is sequenced in search of biosynthetic pathways. The giant milkweed Calotropis gigantea, a flowering shrub that can grow to 13 feet tall, produces a multitude of chemicals that have possible anticancer and antimalarial properties. A new Genome Report published in G3 describes the plant’s genome, providing…
-
Worm studies reveal cells on the move
Consider the papercut—a minor injury best known for the disproportionate amount of pain it can cause. That a wound so inconsequential can sting so terribly is curious, but perhaps even more surprising is the fact that it heals at all. To heal a wound, even one as trivial as a papercut, the cells involved in…
-
How baker’s yeast turns from friend to foe
Beer, doughnuts, and genetics textbooks have one thing in common: they were all made possible by collaborations between humans and yeast. Our fungal ally Saccharomyces cerevisiae resides not only in breweries, bakeries, and laboratories, but also sometimes in our own bodies—where, on rare occasions, it betrays us. S. cerevisiae is increasingly being reported as an…
-
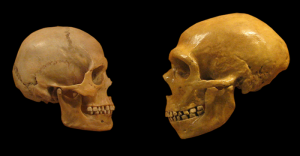
Tales told by ancient human DNA
Archaeologists have long known how to extract millennia-old stories from a single tooth buried in an ancient ruin—and now geneticists have the tools to join them. Advances made in the last several years have enabled researchers to sequence tiny amounts of DNA preserved in very old specimens, such as the material inside a tooth from…