Enter your address to receive notifications about new posts to your email.
Science & Publishing
-
Science & Publishing
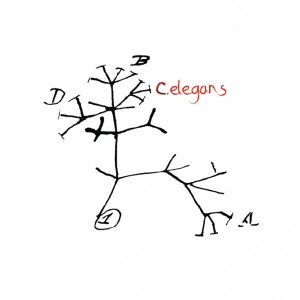
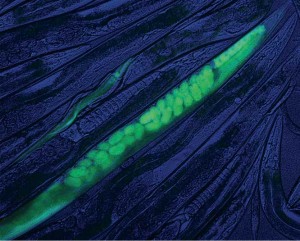
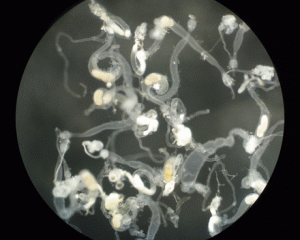
The new genomic world of wild worms
Mark Blaxter (Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh) reports on the “Caenorhabditis Genomes Project” workshop at GSA’s recent 20th International C. elegans Meeting. Caenorhabditis elegans, affectionately referred to as “the worm,” is one of the prettiest and most informative of the model organisms. It is see-through, has a simple lifecycle and a remarkably simple anatomy,…
-
Science & Publishing
August GENETICS Highlights
The August issue of GENETICS is out now! Check out the Highlights below or the full Table of Contents here. ISSUE HIGHLIGHTS Characterizing race/ethnicity and genetic ancestry for 100,000 subjects in the genetic epidemiology research on adult health and aging (GERA) cohort, pp. 1285–1295 Yambazi Banda, Mark N. Kvale, Thomas J. Hoffmann, Stephanie E. Hesselson, Dilrini Ranatunga, Hua Tang, Chiara Sabatti, Lisa…
-
Science & Publishing
GSA pleased to be founding member of Plant Science Research Network
The Genetics Society of America (GSA) is pleased to be a founding member of the Plant Science Research Network (PSRN), which was launched earlier this week. This effort, supported by a Research Coordination Network award from the National Science Foundation (NSF), will seek to unite the plant science community and to harness its collective vision…
-
Science & Publishing
New in G3: CRISPR, C. elegans, & a ciliopathy
Check out the August issue of G3! Perspectives Exome Sequencing: Current and Future Perspectives Amanda Warr, Christelle Robert, David Hume, Alan Archibald, Nader Deeb, and Mick Watson G3 August 2015 5:1543-1550; Early Online July 2, 2015, doi:10.1534/g3.115.018564 Full Text | Full Text (PDF) Investigations Identification of Wnt Pathway Target Genes Regulating the Division and Differentiation of…
-
Science & Publishing
Multiple Paths to the Same Result: Parallel Evolution in Lake Whitefish
For Lake Whitefish, history has repeated itself. Across the St. John River region that spans Québec and Maine, these freshwater fish have continually evolved in the same way. Within the many individual lakes in this area, Lake Whitefish have diverged into two groups differentiated by size and body shape. These two groups, known as “dwarf”…
-
Science & Publishing
A “date” with the history of Phoenix dactylifera cultivation
The sticky fruit of the date palm has a tangled history. New research in G3 explores the palm’s genetic diversity and traces its earliest cultivation to at least two distinct regions in North Africa and the Arabian Gulf. The date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) is one of the world’s oldest cultivated trees and has close ties…
-
Science & Publishing
Worm CRISPR Workshop at the International C. elegans Meeting
Technical tips and progress on worm CRISPR/Cas9 genome engineering Today’s guest post was contributed by Mike Boxem, Daniel Dickinson, and Alexandre Paix. Mike Boxem is a group leader at Utrecht University. His interests include technology development, systems biology, and cell polarity. Daniel Dickinson is a postdoctoral research fellow at the University of North Carolina. His interests include…
-
Science & Publishing
The Secret Sex Lives of the Bdelloid Rotifers
Bdelloid rotifers have been veiled in mystery for decades. Despite extensive studies of this class of tiny freshwater invertebrates, no one has observed any trace of sex: no proven males, hermaphrodites, mating, or meiosis. Unlike other asexual organisms, which tend to be short-lived in evolutionary history, the apparently asexual bdelloid rotifers have managed to persist…
-
Science & Publishing
The mutation that unlocked corn kernels
If not for a single-nucleotide mutation, each kernel on a juicy corn cob would be trapped inside an inedible casing as tough as a walnut shell. In the July issue of GENETICS, Wang et al. identify an amino acid substitution that was key to the development of the so-called “naked” kernels that characterize modern corn…
-
Science & Publishing
New in G3: peanuts, peas, & dates
Check out the July issue of G3! INVESTIGATIONS Multiple Conserved Heteroplasmic Sites in tRNA Genes in the Mitochondrial Genomes of Terrestrial Isopods (Oniscidea) Christopher H. Chandler, Myriam Badawi, Bouziane Moumen, Pierre Grève, and Richard Cordaux G3 July 2015 5:1317-1322; Early Online April 24, 2015, doi:10.1534/g3.115.018283 Abstract | Full Text | Full Text (PDF) | Supporting…
-
Science & Publishing
A genomic balancing act
Allelic expression in the mouse genome is surprisingly unbalanced, according to new research published in the June issue of GENETICS. The factors that determine how a gene is expressed in a given cell are complex. After all, every mammalian cell contains two copies of each gene, and both versions of that gene, called alleles, play…