Enter your address to receive notifications about new posts to your email.
Science & Publishing
-
Science & Publishing
GSA supports open access—but we need time for a full transition
Last Friday, I was made aware of an executive order being finalized by the White House that reportedly mandates immediate public access to journal articles describing federally funded research. If this policy were enacted as is, many scientific societies would have to severely cut their services to the scientific community, such as peer-reviewed journals, travel…
-
Science & Publishing
Coffee and epistasis: a scientific story of sips and SNPs
Guest authors C. Brandon Ogbunugafor and Rafael F. Guerrero demystify higher order epistasis through a short story about the perfect brew. Epistasis is the flavor of the month Epistasis is one of the most popular and provocative topics in modern genetics. It has many different definitions, but one especially useful one is that epistasis is…
-
Science & Publishing
Finding fresh mutations
Improved duplex sequencing identifies spontaneous mutations in bacteria without long-term culturing. Spontaneous mutations are the driving force of evolution, yet, our ability to detect and study them can be limited to mutations that accumulate clonally. Sequencing technology often cannot identify very rare variants or discriminate between bona fide mutations and errors introduced during sample preparation.…
-
Science & Publishing
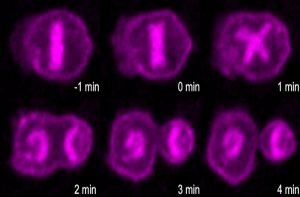
Unequal divisions of death
Apoptotic pathway promotes asymmetric cell division during C. elegans development. Cell division doesn’t always produce identical daughter cells; often, the demands of multicellular development require cells to split into two quite different daughters with quite different fates. These “asymmetric” divisions are needed so that cells can differentiate and specialize, and some cells are even programmed…
-
Science & Publishing
Nested CRISPR for cloning-free fluorescent tags
A better way to make endogenous reporters in C. elegans CRISPR systems for gene editing have revolutionized biological research, but the method still has limitations. While it is usually straightforward to delete parts of the genome using CRISPR, large insertions can be a challenge. This has been the case even for the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans,…
-
Science & Publishing
GSA Journals Spotlight 2018
The GSA Journals, GENETICS and G3: Genes|Genomes|Genetics, are proud to present our annual Spotlight booklets for research published in 2018. Each Spotlight is a showcase of the excellent research and scholarship published over the course of the year, along with a selection of striking images submitted by our authors. Browse the 2018 GENETICS Spotlight. Browse the 2018 G3 Spotlight.
-
Science & Publishing
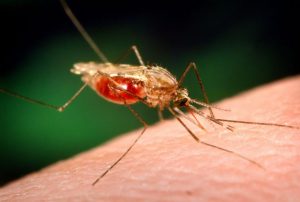
Guest post: Chromosome-scale genome assembly gives African mosquito and malaria vector fewer places to hide its secrets
Guest post by Kathryn “Kaylee” Mueller, Phase Genomics. Plasmodium parasites—the microbes that cause malaria—are right at home in the tropics. After all, tropical regions harbor the two animals that the malaria parasites need to complete their complex lifecycle: female Anopheles mosquitoes and human beings. And in 2017 alone, Plasmodiumracked up 219 million cases of malaria,…
-
Science & Publishing
“Predicting” the future: how genomic prediction methods anticipated technology
A landmark paper published in GENETICS founded the field of genomic prediction before the requisite technology was available. When a new technology is developed, it can allow scientists to make great strides in addressing longstanding questions. Occasionally, however, researchers think so critically about a knowledge gap in their field that they’re able to propose a…
-
Science & Publishing
Three GENETICS articles from 2018 recognized with Editors’ Choice Awards
Congratulations to the winners of the Editors’ Choice Awards for outstanding articles published in GENETICS in 2018! The journal’s Editorial Board considered a diverse range of articles, finding many papers worthy of recognition. After much deliberation, they settled on one exceptional article for each of the three award categories: molecular genetics, population genetics, and quantitative genetics. Check out…
-
Science & Publishing
An ancient regulator of sex development
A Wnt protein involved in the formation of the human ovary plays an important role in female zebrafish sex development. Even though zebrafish are a well-studied research model, how these fish develop into males or females remains rather obscure—in part because the sex of lab strains is not determined by sex chromosomes. Research published…
-
Science & Publishing
Women’s hidden contributions to theoretical population genetics
An analysis of the acknowledgment sections of theoretical population genetics papers from the 1970s and 1980s reveals overlooked contributions of women to the foundation of the field. Theoretical population genetics has a gender imbalance, and it’s easy to get the impression that it’s always been this way. After all, introductory genetics courses emphasize important concepts…