Enter your address to receive notifications about new posts to your email.
Articles by Cristy Gelling (96 results)
-
Luria & Delbrück: Jackpots and epiphanies
In the early 1940s, many biologists doubted bacteria had genes. After all, they seemed to play by their own genetic rules: they appeared to lack chromosomes, meiosis, mitosis, sex, and all the other trappings of Mendelian inheritance. They even seemed to show a kind of Lamarckian inheritance, in which an individual could pass on traits acquired…
-
Evolving butterflies and genome assemblies
The dizzying array of wing patterns in Heliconius butterflies has served as a model for evolution and adaptation in the wild for more than a century. The genus is most famous for the way different species within a geographic region tend to converge on similar wing markings—known as biological mimicry. In the latest issue of…
-
Inducing lifesaving sleep in worms
Sometimes, a nematode worm just needs to take a nap. In fact, its life may depend on it. New research has identified a protein that promotes a sleep-like state in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Without the snooze-inducing molecule, worms are more likely to die when confronted with stressful conditions, report researchers in the March 7, 2016…
-
Dobzhansky: Bug collecting and the Modern Synthesis
In 1917, amidst the turmoil of the Russian Revolution, a bug-obsessed teenager in Kiev discovered a new species of ladybird beetle in the debris washed up on the banks of the flooding Dnieper River. The following year, he described the species in his first scientific publication. That 18-year old ladybug spotter —Theodosius Dobzhansky— would go…
-
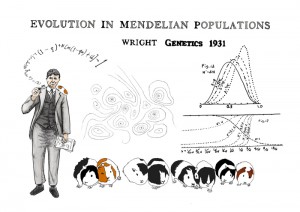
Sewall Wright: Evolving Mendel
In 1931, Sewall Wright—a quiet American geneticist specializing in livestock and guinea pigs—published a GENETICS paper that changed how we study evolution. Wright’s “Evolution in Mendelian populations” was one of the founding documents of population genetics and was among the first formal frameworks to reconcile Mendel’s laws of inheritance with Darwin’s vision of natural selection.…
-
The evolution of Dark-fly
On November 11, 1954, Syuiti Mori turned out the lights on a small group of fruit flies. More than sixty years later, the descendents of those flies have adapted to life without light. These flies—a variety now known as “Dark-fly”—outcompete their light-loving cousins when they live together in constant darkness, according to research reported in…
-
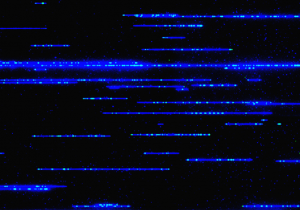
Mapping structural variants with nanochannel arrays
Short-read sequencing has fueled the acceleration of genetic research But though these next-generation methods are fast and efficient, they can’t do everything well. One important area in which short-reads fall short is detecting structural variants (SV), where chunks of the genome are deleted, inserted, repeated, inverted, or in some other way shuffled around compared to…
-
Art & Science: Interview with Alex Cagan
The January cover of GENETICS commemorates the journal’s 100th anniversary and the 1916 publication of Calvin Bridges’ proof that genes lie on chromosomes. The artwork was created by Alexander Cagan, a graduate student at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology studying the genetics of domestication in rats. We spoke to Alex about the cover, his art, and his…
-
Anxious chickens as a model for human behavior
Chickens that “chicken out” in unfamiliar surroundings may shed light on anxiety in humans, according to research published in the January 2016 issue of the journal GENETICS. Domestic chickens are much less anxious than their wild cousins, the red junglefowl. The new research identifies genes that contribute to this behavioral variation and reveals that several…
-
Calvin Bridges: Bringing genes down to earth
When sharp-eyed 20-year-old Calvin Bridges entered Columbia University in 1909, the word “gene” had just been coined. At that time, the term was profoundly abstract, referring to “factors” or “conditions” that could be glimpsed only through the window of statistical analysis. Seven years later, Bridges and his colleagues had brought these mysterious factors firmly down…
-
GENETICS turns 100: marking the past, mapping the future
In 1916, in the very first issue of GENETICS, Calvin Bridges published his proof that genes are carried on chromosomes. One hundred years later, genetics is again at the brink of a major transformation, as efficient genome engineering becomes a reality. During this century of incredible advances, GENETICS, published by the Genetics Society of…